Statistical Innovation for Biomedical Discovery
Welcome to the Zhao Lab in the Department of Mathematics & Statistics at York University (Toronto, Canada). Our research focuses on developing innovative statistical and computational methods for analyzing high-dimensional biological data, with applications in genomics, epigenomics, and precision health. By connecting methodological innovation with real-world biomedical problems, our research advances both fundamental statistical methodology and impactful health discoveries.
🧭 Research Overview
We work at the interface of statistics, genomics, and machine learning, building models that make sense of high-dimensional, noisy, and biologically complex data.
Our current research themes include:
High-dimensional inference in genetic and epigenetic association
Regional DNA methylation QTL mapping using penalized and smooth functional modeling.Wearable omics and dynamic precision health
Integrating wearable sensor data with genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic features for disease phenotyping.
🔬 Regional Methylation Modeling — sparseSOMNiBUS
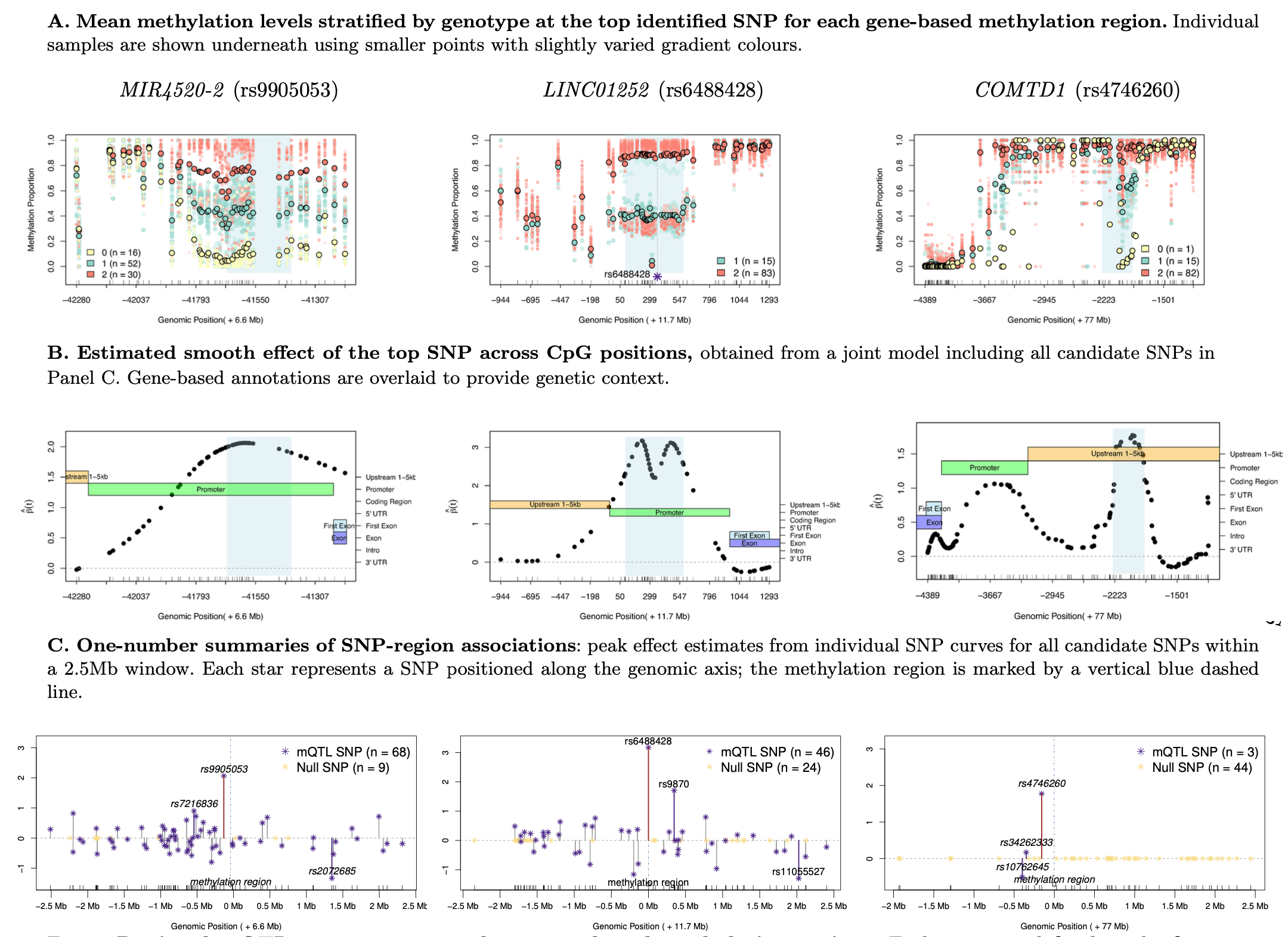
sparseSOMNiBUS (Sparse Smooth Omnibus Model for Regional DNA Methylation QTL Mapping) is our newly published method for identifying regional mQTLs using high-resolution bisulfite sequencing data.
It unifies smooth functional modeling with sparse variable selection, allowing accurate estimation of SNP–CpG associations across genomic regions.
Zhao K, Yang AY, Oualkacha K, Zeng Y, Klein K, Hudson M, Colmegna I, Bernatsky S, Greenwood CMT.
A novel high-dimensional model for identifying regional DNA methylation QTLs.
Biostatistics, Volume 26, Issue 1, 2025, kxaf032.
https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxaf032
📈 Model Illustration
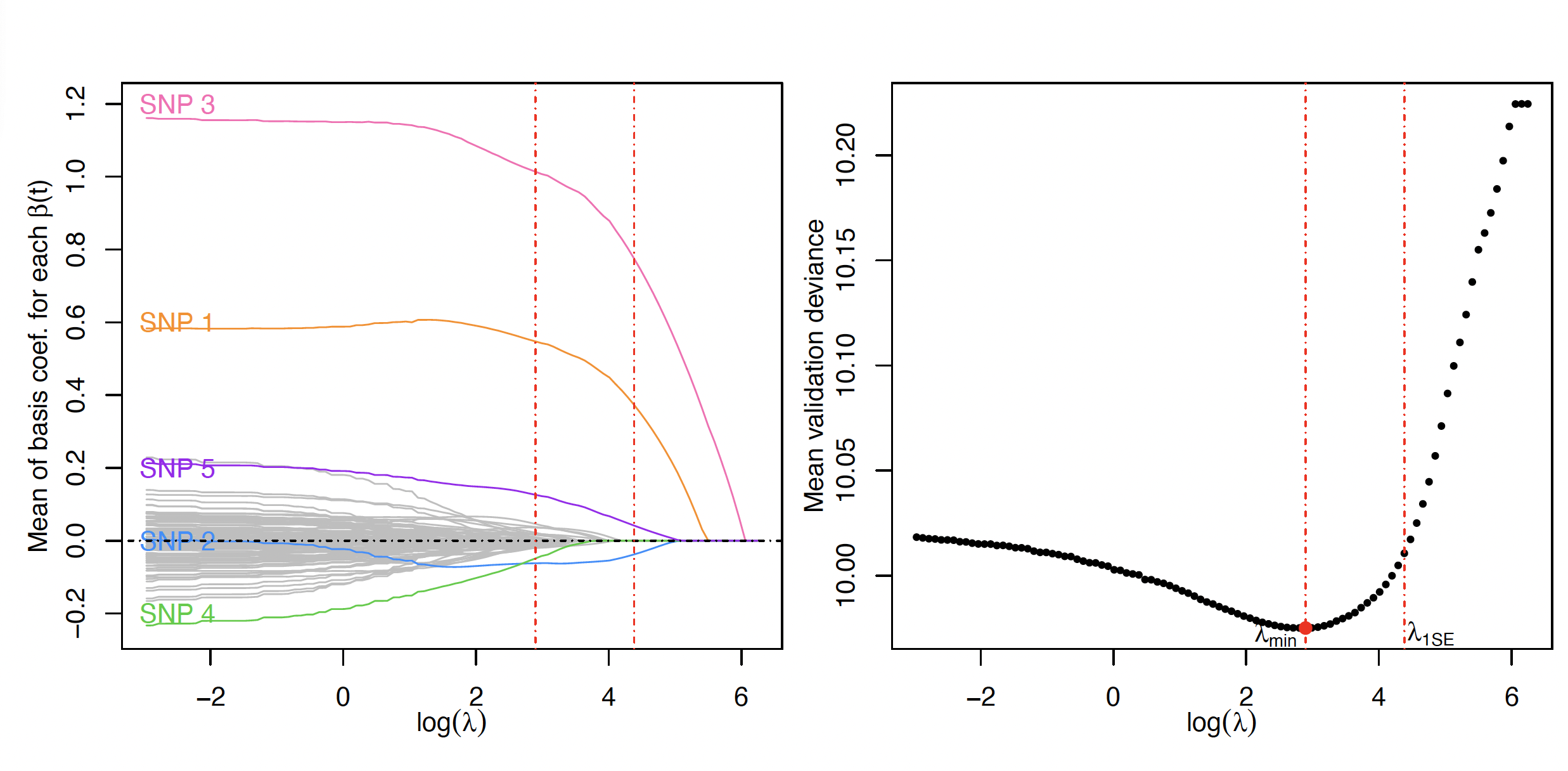
sparseSOMNiBUS fits a penalized regression model balancing smoothness and sparsity.
The tuning parameter λ is selected via cross-validation using both the minimum mean deviance (λ_min) and the 1-SE rule (λ_1SE) to achieve model parsimony and interpretability.
🧬 Sequence-Level Motif Analysis — MoMotif
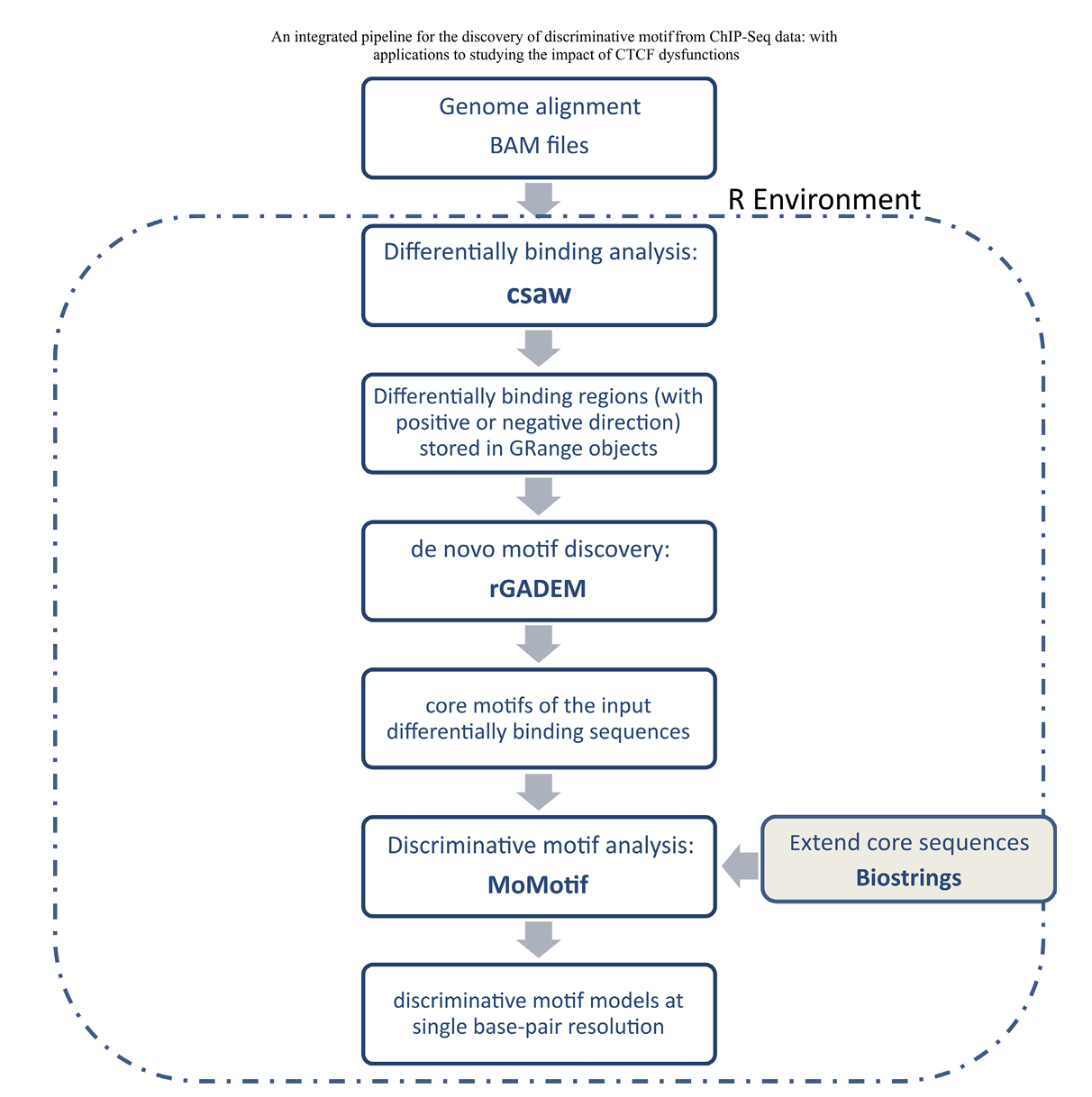
Figure 2 from Lebeau&Zhao et al., NAR 2022 — MoMotif pipeline integrating csaw, rGADEM, and discriminative motif analysis.
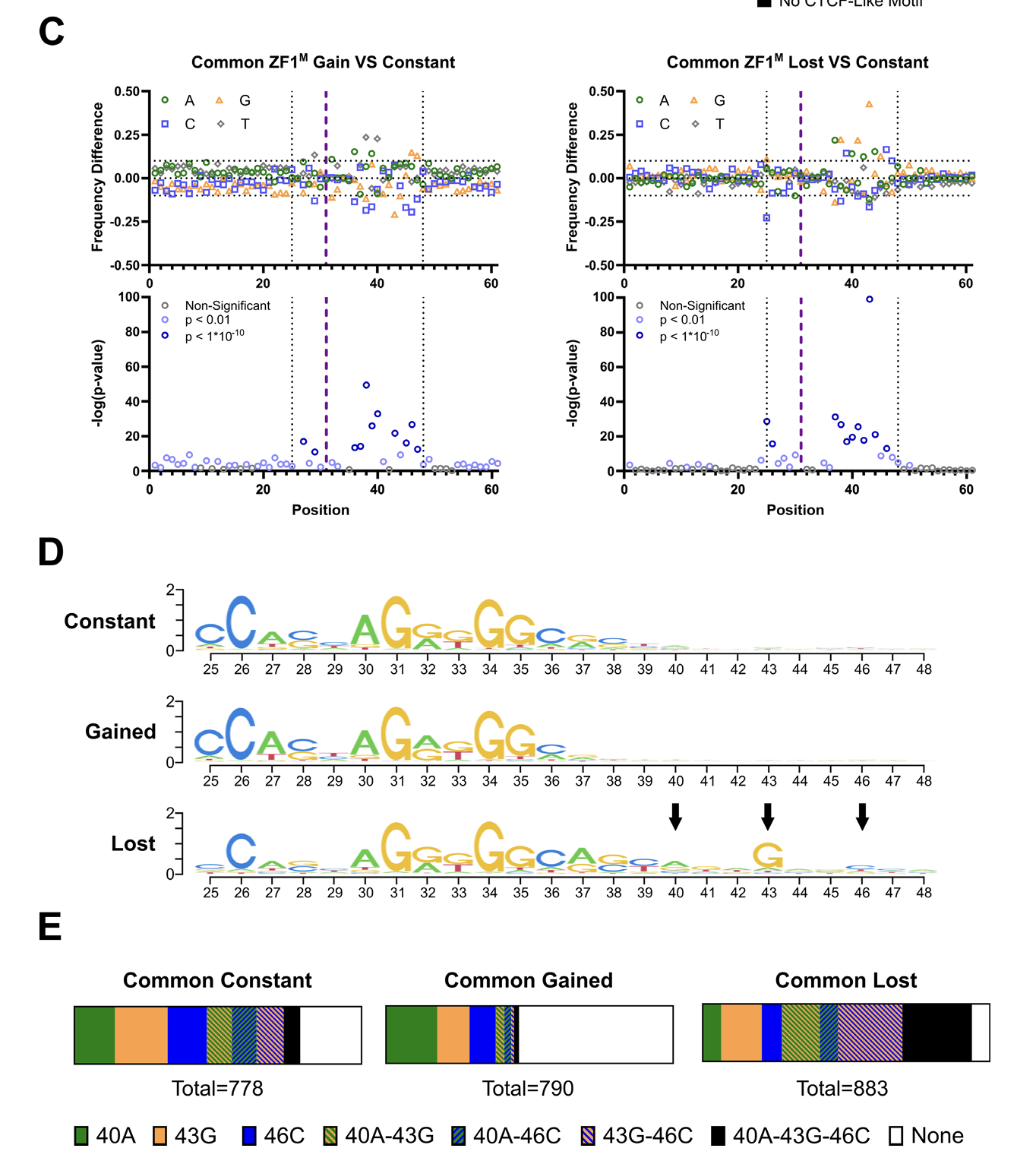
MoMotif identifies extended bases of CTCF motif lost upon KI/KI mutation (base-wise p-value scan and motif logos).
Single base-pair resolution analysis of DNA binding motif with MoMotif reveals an oncogenic function of CTCF zinc-finger 1 mutation
Nucleic Acids Research, 2022.
Lebeau B, Zhao K, Jangal M, Zhao T, Guerra M, Greenwood CMT, Witcher M.
(*co-first authors)
MoMotif is a discriminative motif analysis and visualization framework that identifies condition-specific alterations in transcription factor binding motifs from ChIP-seq data.
It integrates differential binding detection (csaw), de novo motif discovery (rGADEM), and base-wise statistical testing (MoMotif R package) to pinpoint single-nucleotide changes in binding preference across experimental conditions.
Applied to CTCF zinc-finger mutations, MoMotif revealed how a single base change in the genome alters DNA-binding specificity aand can impact local chromatin organization.
This work represents the molecular-scale foundation of our broader research program—linking sequence-level perturbations (MoMotif) to regional methylation modeling (sparseSOMNiBUS) and genome-wide causal inference (ongoing).
🧑🔬 Join Us
We are always looking for motivated students and postdocs interested in:
- Statistical genetics and epigenomics
- Causal inference and Mendelian randomization
- High-dimensional and functional data analysis
- Integrative modeling of multi-omics and wearable data
If you are excited about developing new statistical methods for biomedical discovery, feel free to reach out!
📧 kaiqiong@yorku.ca
